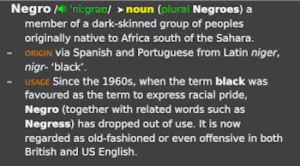
The word Negro is discussed on this date's Registry. This article and its references are written to add to the history of this word.
Negro means "black" in Spanish and Portuguese and is derived from the Latin word niger, of the same meaning. The term "negro", literally the Spanish and Portuguese to refer to Black Africans and people with that heritage used “black.” From the 18th to the mid-20th century, "negro" (later capitalized) was considered the correct and proper term for African Americans. It fell out of favor by the 1970s in the United States.
In current English language usage, "Negro" generally is considered acceptable in a historical context or the name of older organizations, as in the United Negro College Fund, and is used more commonly by those born before the post-World War II baby boom. Lyndon B. Johnson was the last American president to publicly refer to the African American population as Negroes (to which, for much of his life, he gave the Texas pronunciation nigras, widely considered an insult by African Americans). Before he left office, he had also begun to employ the word Blacks. 19th and 20th-century anthropologists used the related word (Negroid) to refer to a race of people from Africa. This ended in the mid-to-late 20th century.
The word has had a similar history in languages such as Italian. In Italy, using the term "negro" to refer to a Black person would be considered a racist insult, suggesting fascist opinions. Yet, in Portuguese, the socially accepted term nowadays is "negro" (literally, "black"), while "preto" (meaning, in this context, "black-skinned") usually is seen as a possible insult because of societal color bias. But, today, some Portuguese people and Portuguese-speaking blacks prefer the term preto in opposition to Branco (white), then negro (that also can mean "dirty"). In French, nègre was generally used in the 19th century and earlier to describe black persons of African origin. It now has heavy colonial undertones, and the word noir (literally, "black") is always used instead, except occasionally when specifically discussing slavery or colonialism or when nègre is used as slang for ghostwriters.
In Argentina and Cuba, Negro (Negra for females) is a word commonly used to refer to friends or people in general and does not have a racist connotation. For example, one may say to a friend, "Oye, negrito. Como estás? That translates as, "Hey, black man, how are you doing?" Here, "negro" is used in its diminutive form, "negrito", as a term of endearment meaning "pal," or "buddy" or "friend." "Negrito" has come to be used to refer to a person of any ethnicity or color, and also can have a sentimental or romantic connotation similar to "sweetheart" or "dear" in English. (In the Philippines, Negrito was used for a local dark-skinned, short people living in the Negros islands, among other places) In other Spanish-speaking South American countries, the word negro can also be employed in a roughly equivalent form. However, it is not usually considered as widespread as in Argentina or Cuba (except perhaps in a limited regional and/or social context). In Cuba, Moreno is used for a Black person. In other parts of the Spanish-speaking world, Moreno means just "tanned," brown, or brunette.
In the Post-Soviet states, the word negr (derived from negro) commonly refers to somebody with African ethnic roots. Because most of the population has seen such people only on television or in films, the word negr has no negative aftertaste. The direct translation of "black" (chjornyj) refers nowadays to people from the southern regions of the former Soviet Union (Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, etc.) and is considered a racist insult. The word cvetnoj ("coloured") is also socially unacceptable in most layers of society. The controversy around the word "Negro" has spread to many languages, to a greater or lesser extent, because many have come to perceive the usage of any word similar to "Negro" concerning black people in any language as a possible form of insult. Internationally, there is no definite consensus.
While some argue that prevailing attitudes in the United States of America (and elsewhere) should not always be taken into account when deciding what words people should use in other languages, others try to avoid using "Negro" or its variants, as they have come to consider that it could be possibly offensive. Implementing this decision is not always easy because, in some languages, the word for "black" is not considered to be a better alternative at all (in Russian, chornyi is a name for minorities like Chechens, in Estonian must also mean "dirty," etc.) Other options are "dark-skinned" or "African."
However, many languages presently do not have widely accepted alternatives for an alternative to "Negro" that is more neutral or positive in its associations. Some Spanish-speaking people have adopted the term "negrito" or even "Azulito" (the diminutive of "Azul," the color blue) instead of "negro" to avoid the insulting connotation of the word in English, especially around English-speaking people who do not know Spanish. A specifically female form of the word negress was sometimes used, but, like another gender-specific word, "Jewess," it has completely fallen from use. Both are considered racist and sexist. In the 1960s, Richard B. Moore created the Committee to present the truth about the Name Negro. He also published the Name “Negro”-Its Origin and Evil Use.
As with other racial, ethnic, and sexual words seen as pejoratives, some individuals have tried "reclaiming" the word. An example of this is artist Kara Walker. In the US, some African Americans may use the term playfully among themselves (as in "You can't please Negroes"), especially throughout the American South and other areas with a higher percentage of blacks. Such usage is similar to the word nigga, although it is generally not considered profanity and is less offensive.